

 about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
Quick Links
Recent Citations
Necroptosis blockade prevents lung injury in severe influenza. Gautam A, Boyd DF et al. Nature. 2024 Apr 25;628(8009):835–843.
Cryogenic electron tomography reveals novel structures in the apical complex of Plasmodium falciparum. Sun SY, Segev-Zarko L-a et al. mBio. 2024 Apr 10;15(4):e0286423.
Conformational ensemble of yeast ATP synthase at low pH reveals unique intermediates and plasticity in F1-Fo coupling. Sharma S, Luo M et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Apr;31(4):657-666.
Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork. Li N, Gao Y et al. Nature. 2024 Mar 28;627(8005):890–897.
Comprehensive mutational scanning of EGFR reveals TKI sensitivities of extracellular domain mutants. Hayes TK, Aquilanti E et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 28;15(1):2742.
Previously featured citations...Chimera Search
Google™ SearchNews
October 30-31, 2023
Planned downtime: The Chimera and ChimeraX websites and associated web services will be unavailable Oct 30 8am PDT – Oct 31 11:59pm PDT.
April 19, 2023
Chimera production release 1.17.1 is now available, fixing an issue with 1.17 for Windows and Linux. See the release notes for details.
April 13, 2023
Chimera production release 1.17 is now available. Updating is required to keep using the tools that run Blast Protein, Modeller, and multiple sequence alignment with Clustal Omega or MUSCLE, as these will soon stop working in older versions. See the release notes for details.
Previous news...Upcoming Events

UCSF Chimera is a program for the interactive visualization and analysis of molecular structures and related data, including density maps, trajectories, and sequence alignments. It is available free of charge for noncommercial use. Commercial users, please see Chimera commercial licensing.
We encourage Chimera users to try ChimeraX for much better performance with large structures, as well as other major advantages and completely new features in addition to nearly all the capabilities of Chimera (details...).
Chimera is no longer under active development. Chimera development was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (P41-GM103311) that ended in 2018.
Feature Highlight
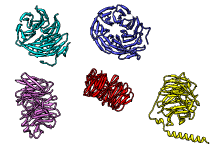
There are several ways to superimpose structures in Chimera:
•
MatchMaker performs a fit after automatically identifying
which residues should be paired.
Pairing uses both sequence and secondary structure,
allowing similar structures to be superimposed even when
their sequence similarity is low to undetectable.
The figure shows five distantly related proteins
(pairwise sequence identities <25%) from the
SCOP WD40 superfamily before and after
MatchMaker superposition with default parameters.
•
Structures can be matched
using a pre-existing sequence alignment.
•
The exact atoms to pair can be specified with the
match command.
This works on any type of structure, while the preceding methods
apply only to peptide and nucleotide chains.
•
Structures can be superimposed manually by
activating/deactivating them for motion and
using the mouse.
Gallery Sample
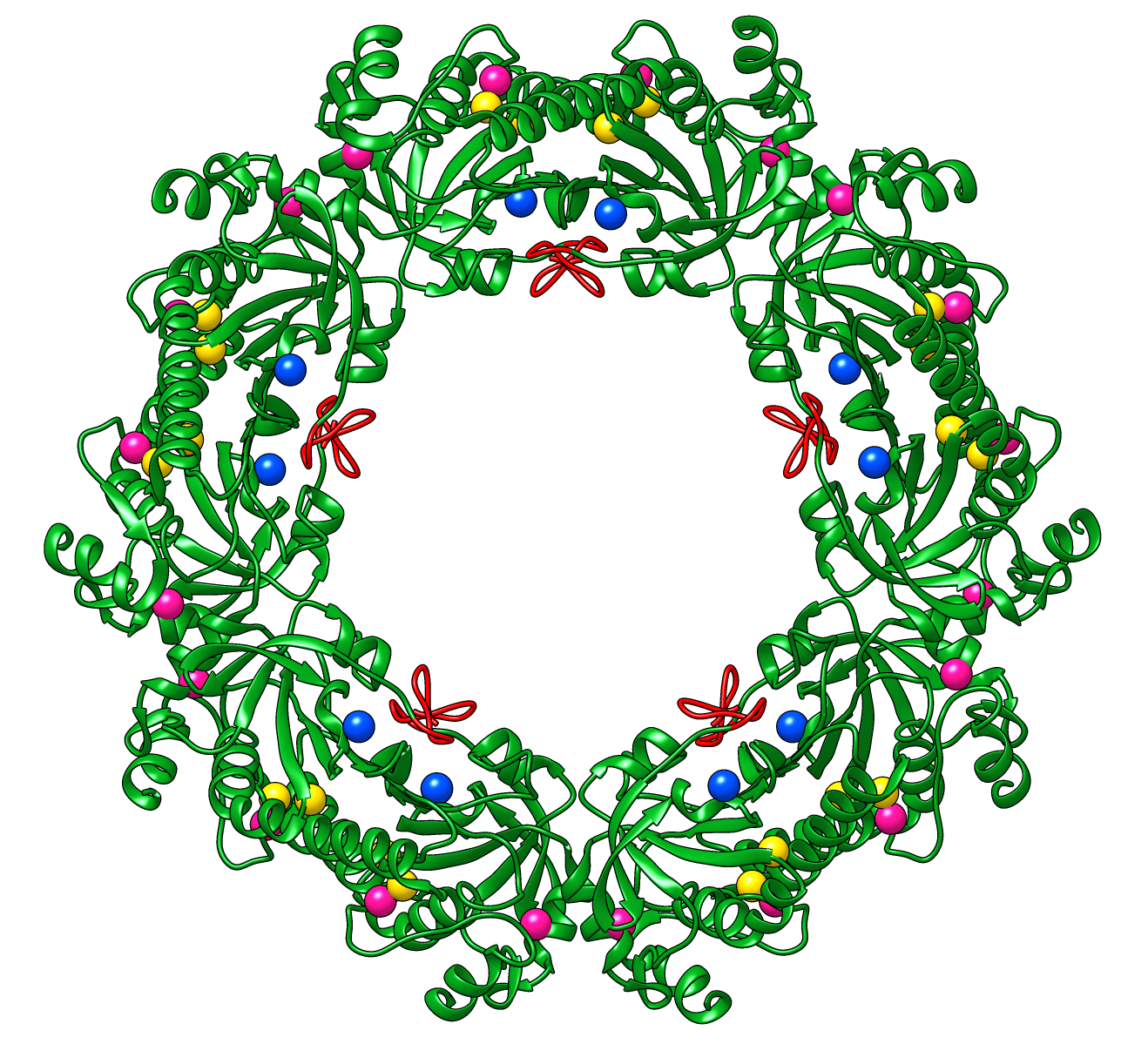

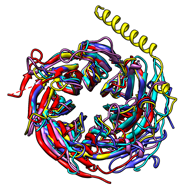
Peroxiredoxins are enzymes that help cells cope with stressors such as high levels of reactive oxygen species. The image shows a decameric peroxiredoxin from human red blood cells (Protein Data Bank entry 1qmv), styled as a holiday wreath.
See also the RBVI holiday card gallery.
About RBVI | Projects | People | Publications | Resources | Visit Us
Copyright 2018 Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.